A Wav2Vec 2.0 implementation using PyTorch Lightning. This project aims to create a clean, modifiable building block for speech reco
gnition research. It uses common tools for optimized training and effective monitoring. The implementation includes code for model training, dataset preparation, and evaluation. This page also details the results of pretraining on the Libri-Speech dataset.
Architecture
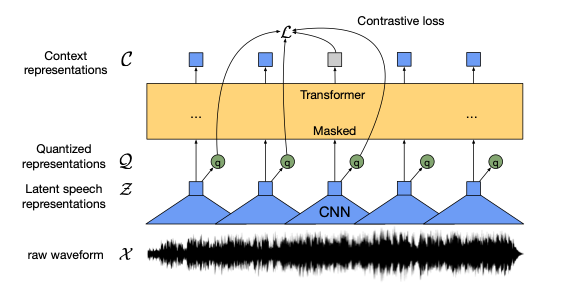 My implementation closely follows the Wav2Vec 2.0 BASE model architecture:
My implementation closely follows the Wav2Vec 2.0 BASE model architecture:
- 768 embedding size
- 8 attention heads
- 12 transformer blocks
- 512 convolutional channels in the feature encoder
- 2 groups and 320 choices per group in the quantizer
This configuration results in approximately 95M parameters. The model processes raw audio waveforms, first through a convolutional feature encoder, then applies quantization, and finally processes the representations through a transformer to produce contextualized representations.
Wav2Vec2Base(
(feature_encoder): FeatureEncoder(
(conv_layers): ModuleList(
(0): Sequential(
(0): Conv1d(1, 512, kernel_size=(10,), stride=(5,), padding=(4,), bias=False)
(1): GroupNorm(32, 512, eps=1e-05, affine=True)
(2): GELU(approximate='none')
)
(1-4): 4 x Sequential(
(0): Conv1d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3,), stride=(2,), padding=(1,), bias=False)
(1): Identity()
(2): GELU(approximate='none')
)
(5-6): 2 x Sequential(
(0): Conv1d(512, 512, kernel_size=(2,), stride=(2,), bias=False)
(1): Identity()
(2): GELU(approximate='none')
)
)
)
(feature_projection): ...
(positional_embedding): ...
(transformer): ModuleList(
(0-11): 12 x TransformerBlock(
(attn): SelfAttention(
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(mlp): MLP ...
(ln_1): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(ln_2): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(ln_f): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
(quantizer): VectorQuantizer(
(projector): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=640, bias=True)
)
(out_linear): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
)
Pretraining
Optimization Techniques
The implementation incorporates several optimization techniques:
- Mixed Precision: BF16 mixed precision for computational efficiency and reduced memory usage.
- Gradient Clipping: Set to 1.0 to prevent exploding gradients.
- DDP (Distributed Data Parallel): Enables parallel processing on multiple GPUs, significantly accelerating training times.
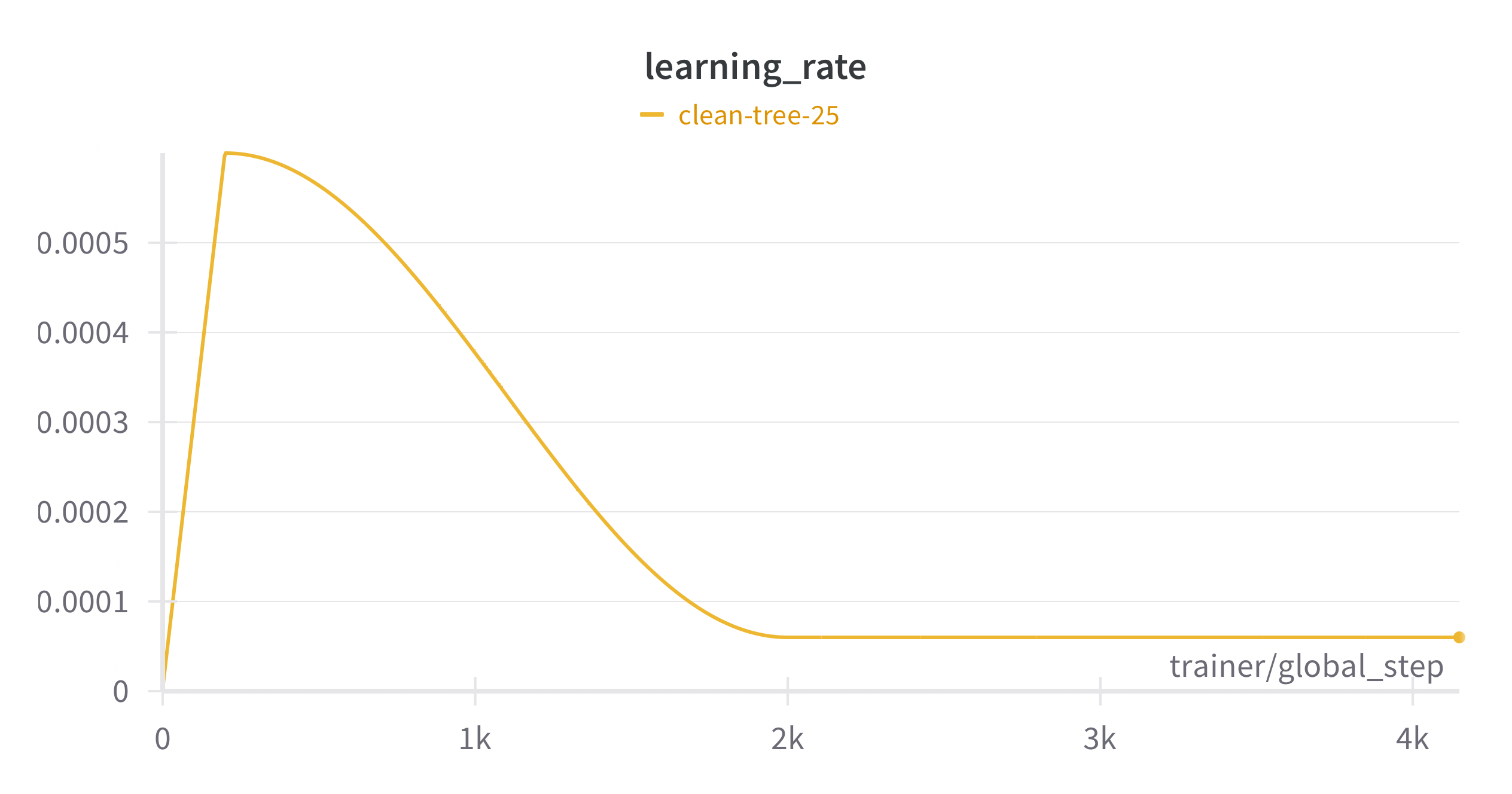
- Scheduled Learning Rate: Warmup and cosine annealing like in the GPT-3 paper
Dataset
For pretraining, we use the LibriSpeech dataset, which consists of about 960 hours of English speech. The dataset is processed in streaming mode to handle large amounts of data efficiently.
Example:
Quantization and Loss
The model uses a Vector Quantizer to discretize the latent representations. This quantization is crucial for the contrastive loss used in pretraining. The loss function combines a contrastive loss, which identifies the correct quantized representation among distractors, and a diversity loss, which encourages the use of the full codebook.
Pretraining Process
The pretraining process follows these steps:
- The raw audio is passed through the feature encoder.
- A proportion of the encoded features are masked.
- The model attempts to predict the correct quantized representations for the masked time steps.
- The loss is computed based on the model’s predictions and the actual quantized representations.
Model Parameters
Key parameters of the model include:
- n_layer: 12 (transformer blocks)
- n_head: 8 (attention heads)
- n_embd: 768 (embedding dimension)
- ffn_dim: 3072 (feed-forward network dimension)
- max_seq_len: 1024
- conv_channels: 512 (in the feature encoder)
- conv_kernel_sizes: (10, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2)
- conv_strides: (5, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2)
- dropout: 0.1
- pos_conv_kernel: 128 (for positional embeddings)
- pos_conv_groups: 16 (for positional embeddings)
Results
TBD..
Fine-tuning
While the current implementation focuses on pretraining, fine-tuning capabilities are planned for future updates. This will allow the model to be adapted for specific speech recognition tasks.
How to Use This Implementation
For detailed instructions on how to use this implementation, refer to the GitHub repository.